Data Science & Big Data Analytics
We live in a complex era, where cities, mobility networks and information systems are increasingly interconnected. In this context, simple sectoral approaches no longer meet the evolving decision-making needs of public administrations and urban operators.
Alongside the vast amount of data now available, there is a growing need for multidimensional (spatial, temporal, sociodemographic and cultural) analyses, which integrate the diverse disciplines and data sources to support informed and strategic choices.
MIC-HUB develops analytical and data-driven approaches to generate new understanding and inform, enrich and guide decision-making processes in the fields of sustainable mobility, urban development and liveable cities.
Using advanced spatial analysis models and machine learning algorithms, the team defines metrics and indicators to improve understanding of mobility dynamics and identify effective solutions for safer, better connected, and more efficient urban environments.
Our analyses include the study of mobility flows across multiple scales and transport modes, evaluations of pedestrian and vehicular densities, travel patterns and road user behaviours, as well as crash data to support targeted safety interventions in diverse urban contexts.
Thanks to advanced data visualisation tools, MIC-HUB transforms complex analyses into clear practical insights, which inform the data, design and decision-making.
Advanced Spatial Analysis with Big Data
Machine Learning with Big Data
Advanced Spatial Analysis with Big Data
The company has extensive experience in advanced spatial analysis and data visualisation using Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Our work in this area integrates spatial and temporal high-resolution big data with other data sources which are more static to deliver a comprehensive understanding of urban dynamics and mobility behaviours.
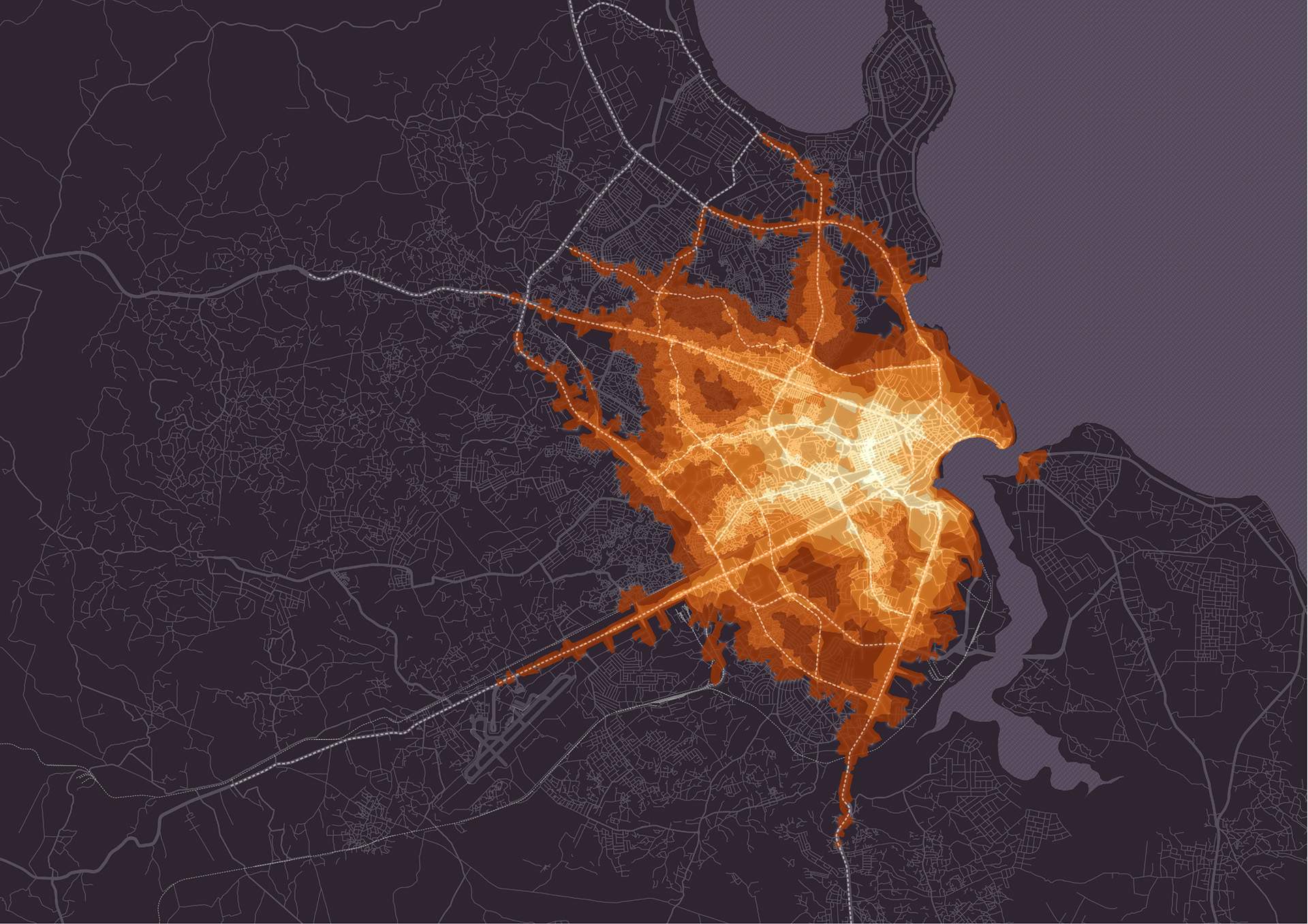
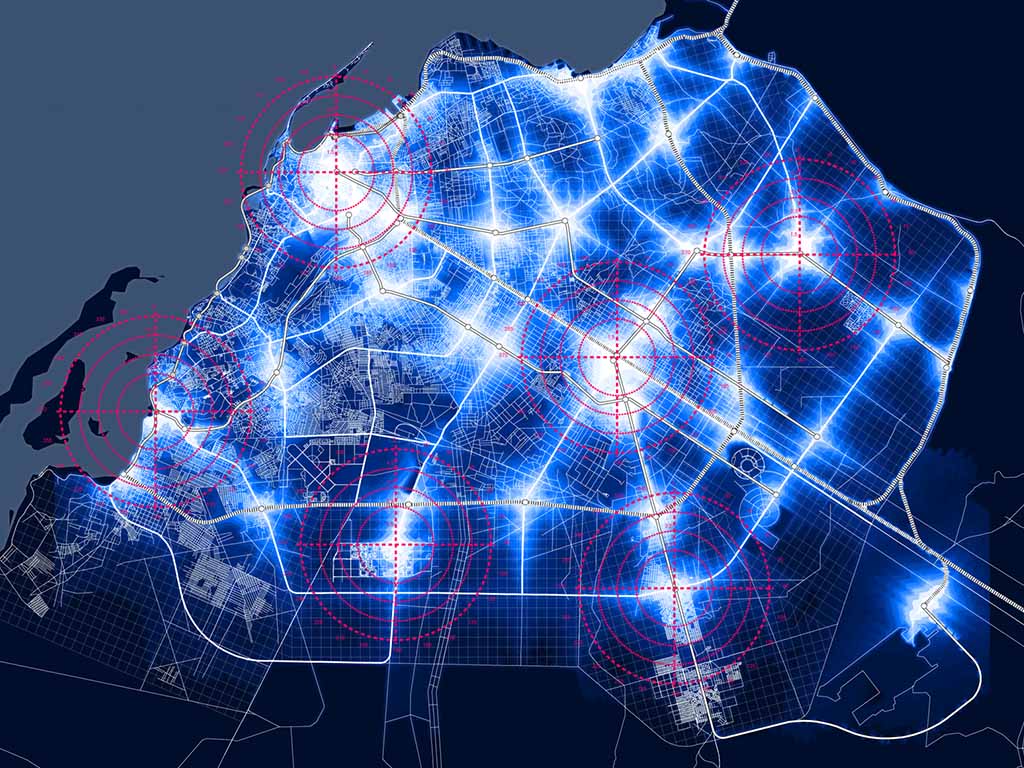
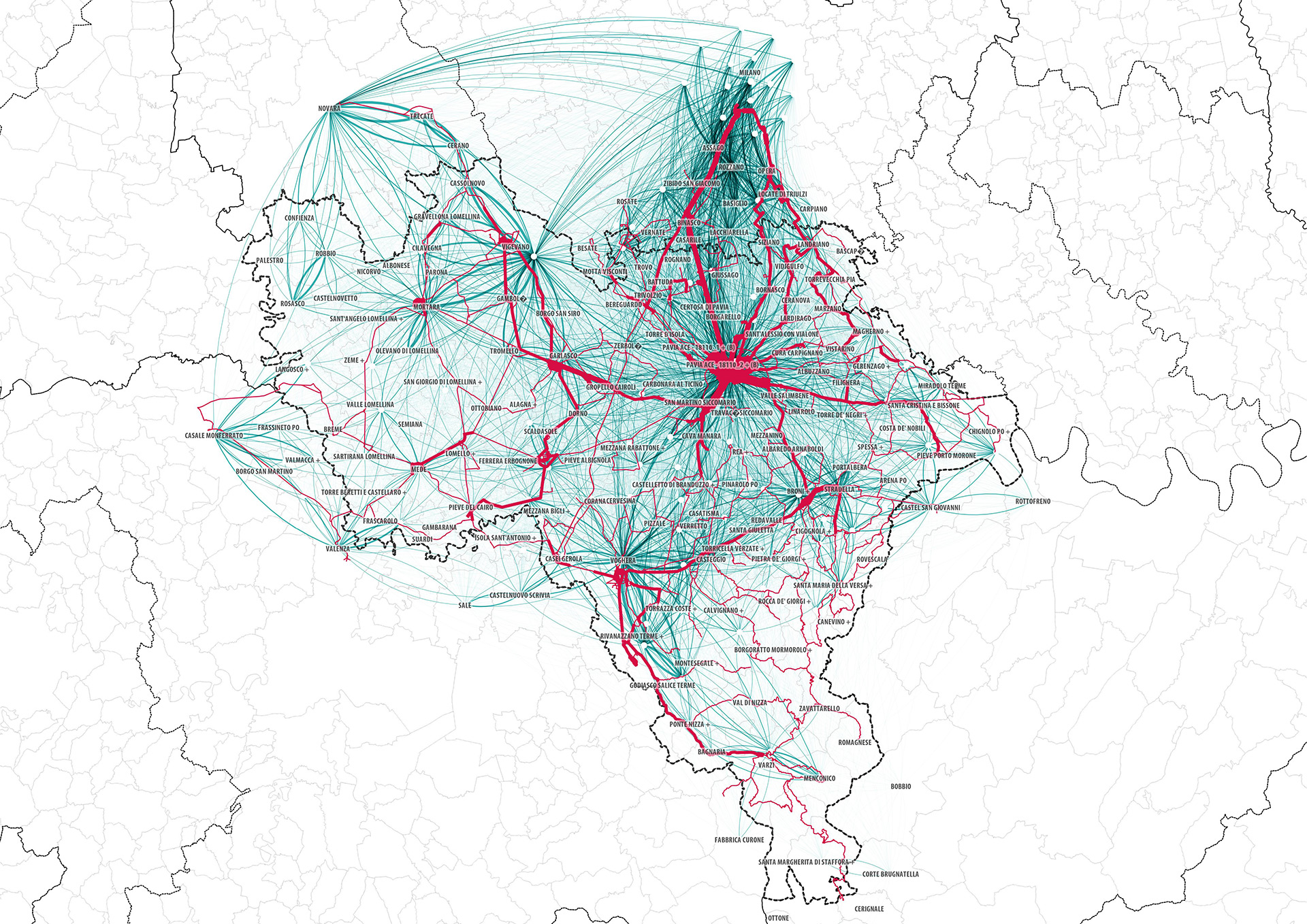
MIC-HUB develops urban activation maps, origin–destination flow maps, and temporal signatures that describe inflow and outflow patterns around major urban attractors.
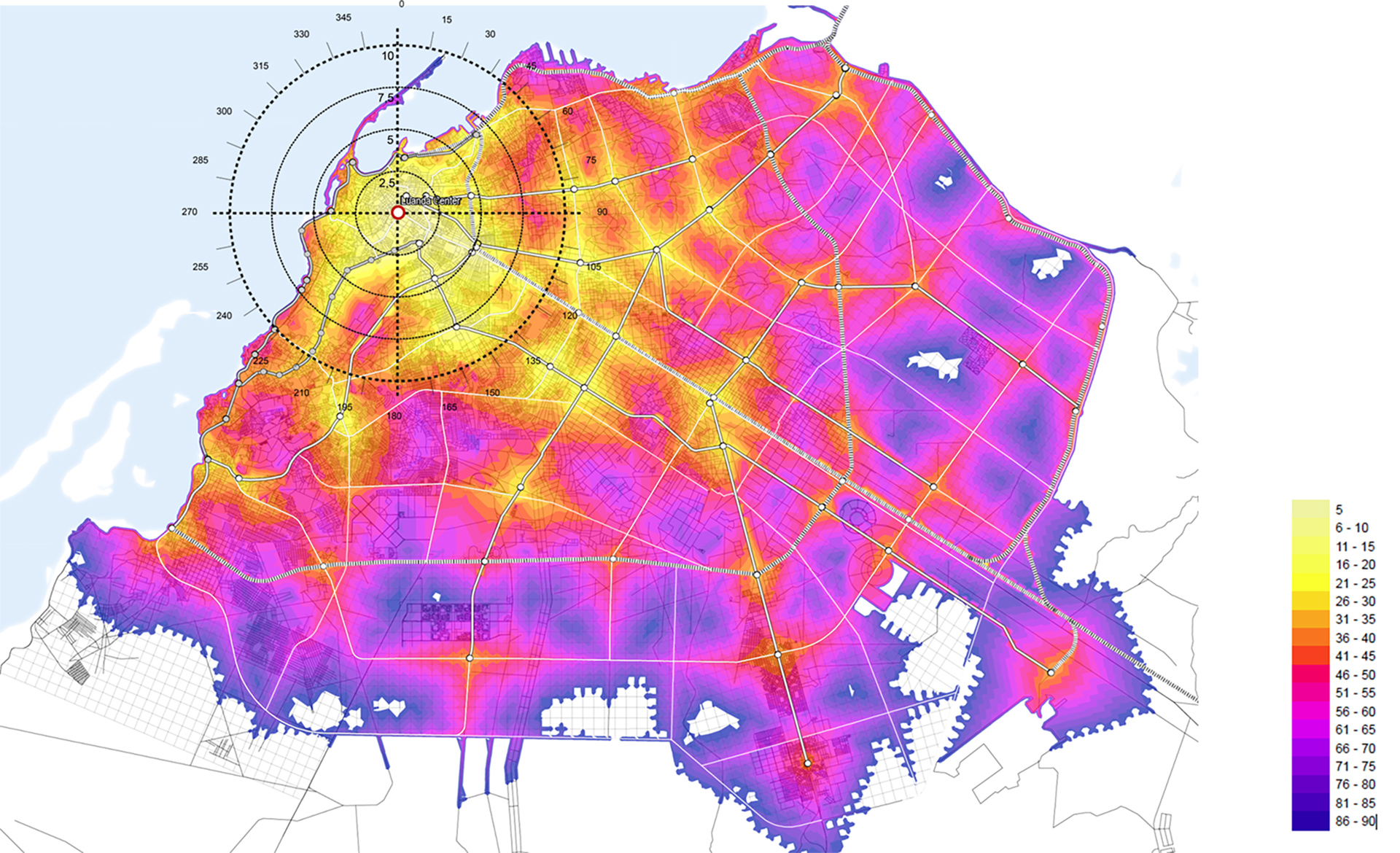
Read moreInternationally recognised metrics, such as PTALs (Public Transport Accessibility Levels) developed by Transport for London, as well as Space Syntax indicators like betweenness are incorporated in the spatial analyses to assess network connectivity and efficiency. MIC-HUB also uses evaluation metrics like Walkscore or other proprietary metrics to assess walkability of the urban space, with the aim of developing active mobility and enhancing the quality of urban environment.
Read lessGeographic Information Systems (GIS)
Analysis of network flows, pedestrian and vehicle density
Spatial and temporal signatures
Public Transport Accessibility Levels (PTAL)
Walkability and accessibility metrics
See the projects
Machine Learning with Big Data
MIC-HUB develops machine learning (ML) algorithms and models to analyse urban mobility phenomena and their interaction with the built environment, providing predictive tools to support decision-making and sustainable mobility planning. MIC-HUB’s models can predict traffic flows, travel behaviours, and road safety risk levels by processing big data from sensors, GPS, social media, and traffic simulations. This contributes to greater efficiency, safety and sustainability in transport systems.
ML algorithms help decode the relationships between mobility and the built environment in terms of urban density, land use, and street design, revealing how these factors influence travel choices, distances, transport modes, and externalities such as crash rates and emission levels.
Read moreMIC-HUB uses supervised learning algorithms, including neural networks, to develop predictive models that assess traffic volumes, network speeds, and accident rates, based on the urban and sociodemographic characteristics of each study area.
Unsupervised machine learning techniques use cluster analysis and dimensionality reduction to identify unknown patterns. These analyses help to reveal hidden structures within complex, heterogeneous data on mobility and other urban characteristics, such as chains of human movement.
Read lessNeural networks
Predictive models
Mobility patterns
Automatic learning of user behaviour
Road safety risk levels
See the projects
![[:en]Pedestrian isochrone accessibility at metro stations in Moscow[:it]Accessibilità isocrona pedonale alle stazioni della metropolitana di Mosca[:]](https://www.mic-hub.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Pedestrian-isochrone-accessibility-at-metro-stations.jpg)